Disclaimer:
This page is not intent for commercial use; all information on this individual page (frame) is direct extraction from academic works to describe the pathology of individual prognosis. The intention of this page is to raise awareness to the general public for the implicated scientific findings.
2. 一般治療方法
a. 尋常性痤瘡(暗瘡)
目前,暗瘡分為基本性治療(過氧化苯甲酰[一般暗瘡膏],維甲酸,抗生素)、系統性治療(口服避孕藥,安體舒通,醋酸環丙孕酮,氟他胺)和物理治療(病灶清除和光學療法)。 [1]
光學療法能分為舊式的UV療程及新形的藍光療程。根據英國倫敦帝國學院科學院的一項藍光療程臨床報告指出 –“ …In our study the mean improvement was 45% (95% confidence interval 32±59) in comedones and 63% (95% confidence interval 52±74) in inflammatory lesions using a cumulative blue light dose of 320J/cm2…. (根據測試,95%的參與者會有平均45%的暗瘡數量減少及63%的炎症減少)“。 [2]
b. 過敏性皮炎(濕疹)
根據”美國過敏,哮喘,免疫學和敏感學學院和歐洲敏感和臨床免疫學學院”指出,過敏性皮炎(濕疹)的典型治療步驟如下:
圖1:過敏性皮炎(濕疹)患者的治療管理。 TCS,外用皮質類固醇; TCI,外用鈣調神經磷酸酶抑製劑環;孢素A,環孢素A *在2歲以上患者。 [3]
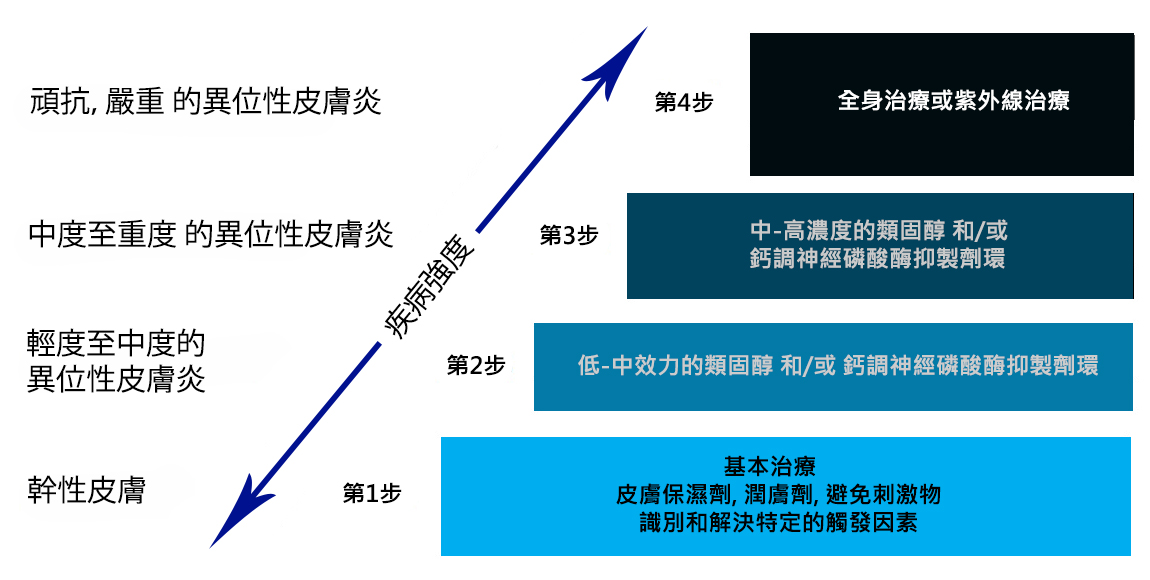
現時大部分的過敏性皮炎(濕疹)患者都依賴類固醇消炎TSC/ TCI藥物控制病情或以UV作出根治。但由於這些治療方色潛在具大副作用,所以不是一項“完美解決方案”。
如上頁所提及,過敏性皮炎(濕疹)發病的其中最大原因是因抗藥性金黃色葡萄球菌(MRSA)些導至。而根據英國斯特拉斯克萊德大學(University of Strathclyde)的研究指出,405nm的藍光有效控制、消滅革蘭氏陽性細菌包括抗藥性金黃色葡萄球菌(MRSA)。這藍光技術再由德國約翰內斯古騰堡大學再作臨床試驗:科學家使用400nm – 450nm的藍光治療36個患者,經過3個月/6個月的測試,患者都有41%/51%的發病減小(EASI計算方式“[4]。
c. LED, 光學治療的方案?
先前的研究顯示400nm-450nm的光學療治療能處理暗瘡和過敏性皮炎(濕疹)。現時有許多LED照明燈能發出400nm的光,,但是現時沒有相關藍光產品特到FDA批准銷售*;這是因為400nm的藍光非常靠近UV區域(399.999nm)而技術上,LED的發光穩定性未能達到醫療標準:
- 一般藍光LED是以銦鎵混合物來做成半導體來做成量子阱和發光[6]。雖然LED是一種高效能的光源,但LED同時很容易受到使用環境和使用時久而影響光能輸出。根據研究,LED的光能輸出會受到環境溫度而影響[7],所以LED在光學治療的使用受到質疑。在另一項研究中,LED對電流(毫安差距)可導至高達10nm的波長差距[8];在400nm的治療中,10nm可導至UV(399.99)風險。
- 藍光LED的銦鎵混合物在使用時會產生調幅分解(spinodal decomposition),成分的拉動 (compositional pulling effect)和表面偏析(surface segregation effect)等物理現像;這些物理現像會做成高達20%的損耗[9]並回做成量子阱和光波段的不穩定。
c. QBM 光學治療衣,能确保光波穩定性和UV安全性嗎?
QBM光學治療衣的特選濾光波段效能亦回隨著時間減低,所以建意在洗滌40次後更換(否則不能确保特選濾光波段的供能)。雖然不能确保特選濾光波段的供能,但是QBM治療衣的阻隔紫外光UV效能絕不減少(經測測效,QBM Blue 的UPF值是至少270)。
*May vary by region
[1] Rathi, S., 2011. Acne Vulgaris Treatment : The Current Scenario: Indian Journal of Dermatology. [PDF] Available at:<http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3088940/> [Accessed 20-01-2013]
[2] Papageorgiou, P., Katsambas, A., Chu, A., 2000. Phototherapy with blue (415 nm) and red (660 nm) light in the treatment of acne vulgaris: British Journal of Dermatology. [PDF] Available at:< http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10809858> [Accessed 20-01-2013]
[3] Akdis, C.A., Akdis, M., Beiber, T., Boguniewicz, M., Eigenmann, P., Hamid, Q., Kapp, A., Leung, D.Y.M., Lipozencic, J., Luger, T.A., Muraro, A., Novak, N., Platt-Mills, T.A.E., Rosenwasser, L., Scheynius, A., Simons, F.E.R., Spergel, J., Turjanmaa, K., Wahn, U., Weidinger, W., Werfel, T., Zuberbier, T., 2006. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/PRACTALL Consensus Report. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. [PDF] Available at: <http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01153.x/pdf> [Accessed 24-12-2012]
[4] Anderson, J., Macgregor, S.J., Maclean M., Woosley, A.G., 2008. Inactivation of Gram-Positive Bacteria. University of Strathclyde. [Patent Application] Available at: <http://www.google.com/patents/EP1924323A1?cl=en >[Accessed 27-12-2012]
[5] Becker, D., Langer, E., Seemann, M., Seemann, G., Fell, I., Saloga, J., Grabbe, S., Stebut, E.V., 2011. Clinical Efficacy of Blue Light Full Body Irradiation as Treatment Option for Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Department of Dermatology, University Medicine, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany. [PDF] Available at: < http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3110790/pdf/pone.0020566.pdf> [Accessed 26-12-2012]
[6] Light-emitting diode: Wikipedia. [Website] Available at:< http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode > [Accessed 26-12-2012]
[7] Narendran, N., Gu, Y., Freyssinier, J.P., Deng, L., 2004. Solid State Lighting: Failure Analysis of White LEDs: Journal of Cystal Growth.[PDF]Available at:<http://www.streetlightingresearch.net/programs/solidstate/pdf/narendran2004_jcrystalgrowth.pdf> [Accessed 26-12-2012]
[8] Yu, S.F., Chang, S.J., Chang S.P., 2012. Investigation of Efficiency Droop for InGaN-based LEDs with Carrier Localization State and Polarization Effect: Institute of Microelectronics & Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University. [PDF] Available at:< http://gaasmantech.com/Digests/2012/papers/12.5.103.pdf>[Accessed 26-12-2012]
[9] Kim, H.J., Shin, Y., Kwon, S.Y., Kim, H.J., Choi, S., Hong, S., Kim, C.S., Yoon, J.W., Cheong, H., Yoon, E., 2008. Compositional analysis of In-rich InGaN layers grown on GaN templates by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition: Journal of Crystal Growth. [PDF] Available at:< http://hompi.sogang.ac.kr/opto/pdf_files/122_Journal%20of%20crystal%20growth_310_3004.pdf>[Accessed 26-12-2012]









Follow us