QBM BLUMOD
It is clinically proven that 400nm range direct light exposure is effective on treating Acne Vulgaris and Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema).
QBM Blue Phototherapeutic garment is a FDA approved Blue visible light therapy solution that can be used to allow the transmittance of 400nm - 450 nm range light, which allow the treatment of Acne Vulgaris, and Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema).
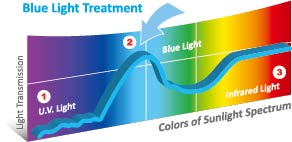
Figure 1: Transmittance of QBM Blue
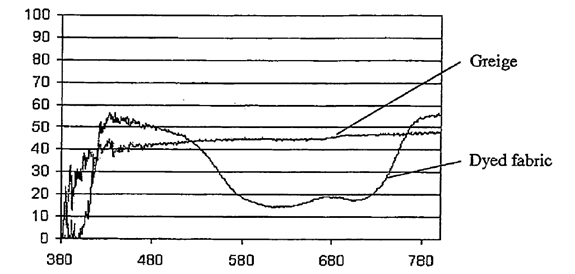
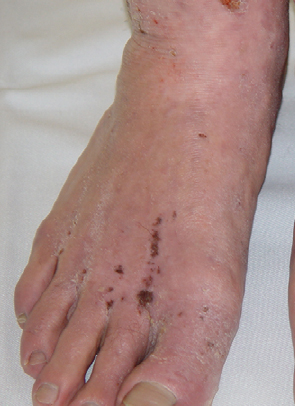
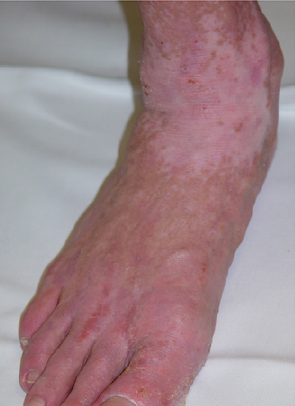
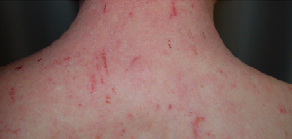
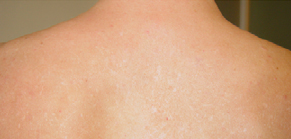
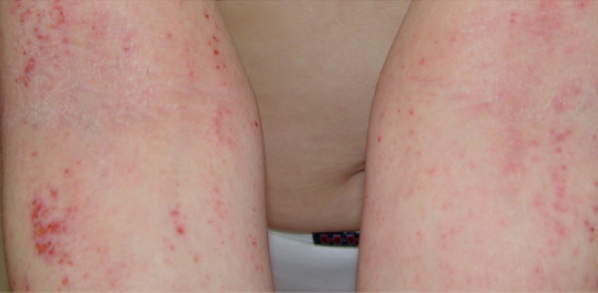
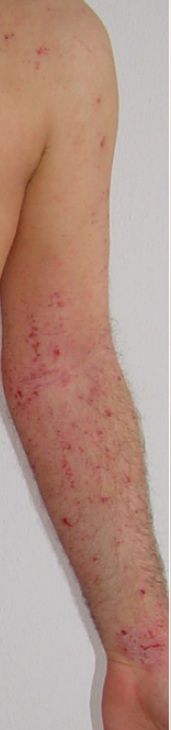
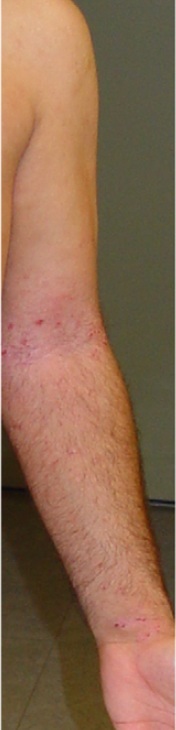
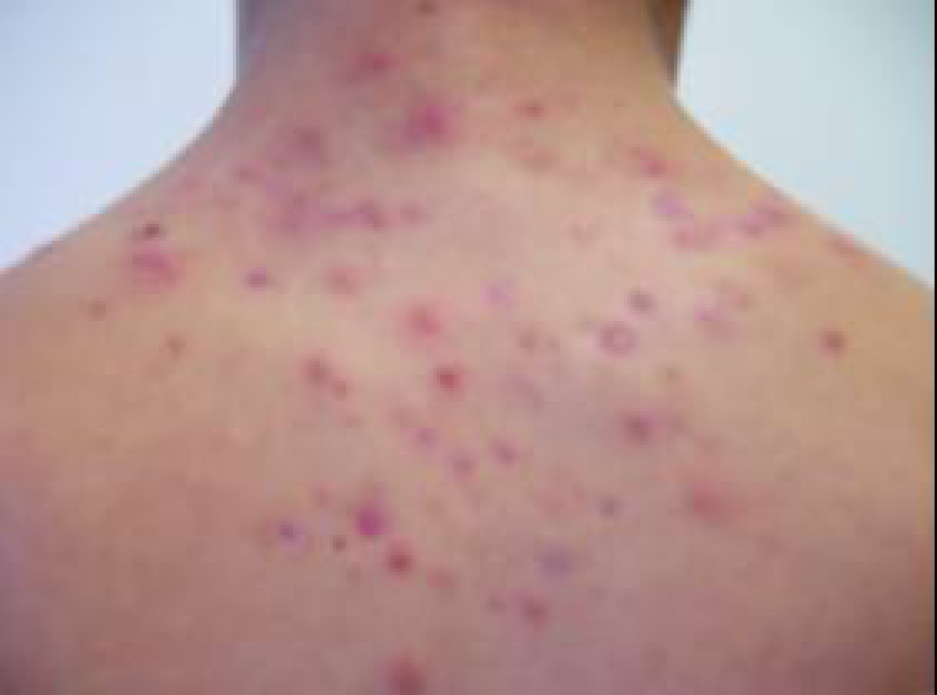
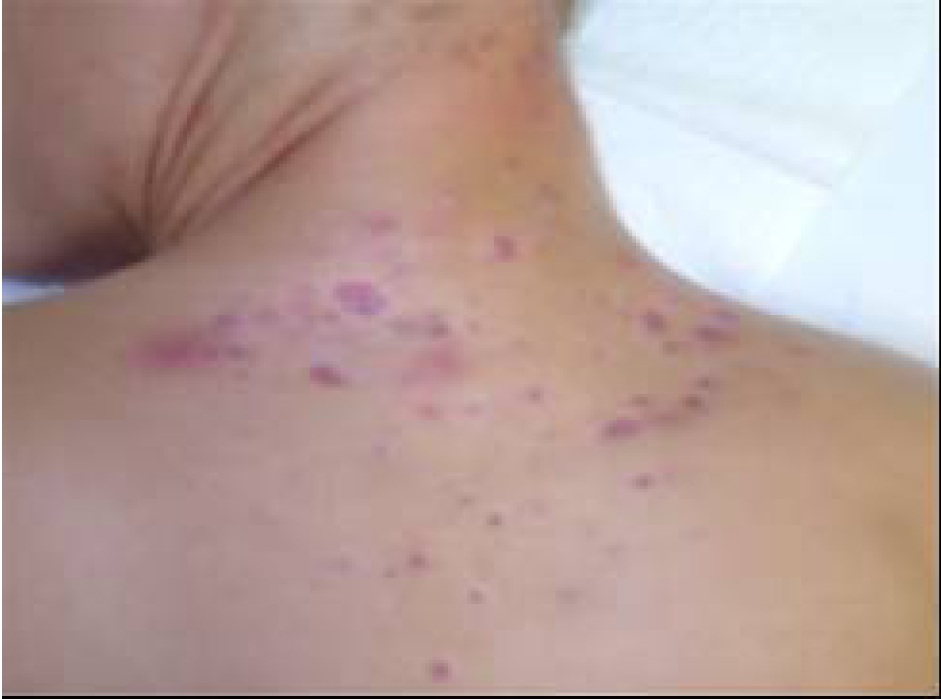
Figure2: Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) Clinical Trial 400nm – 450nm Blue[1]
| Before | After |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
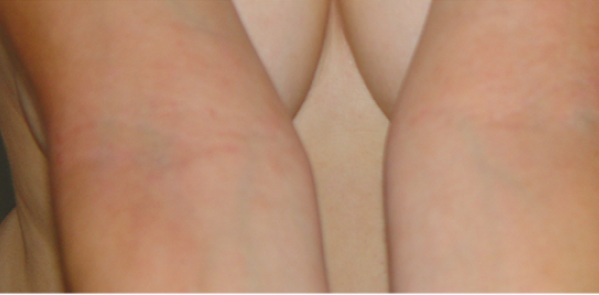 |
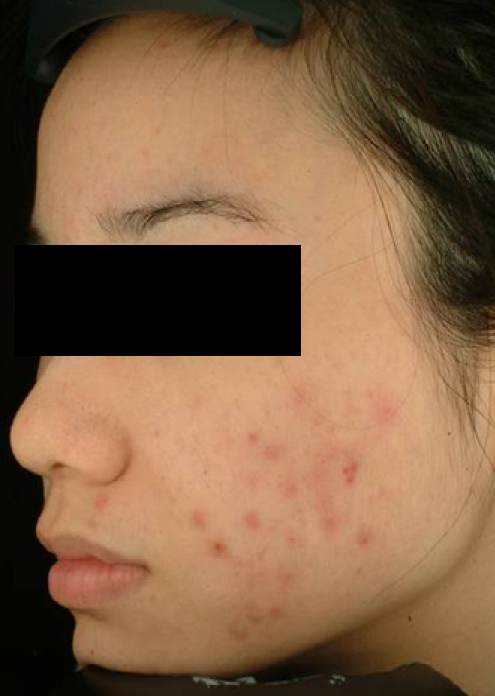
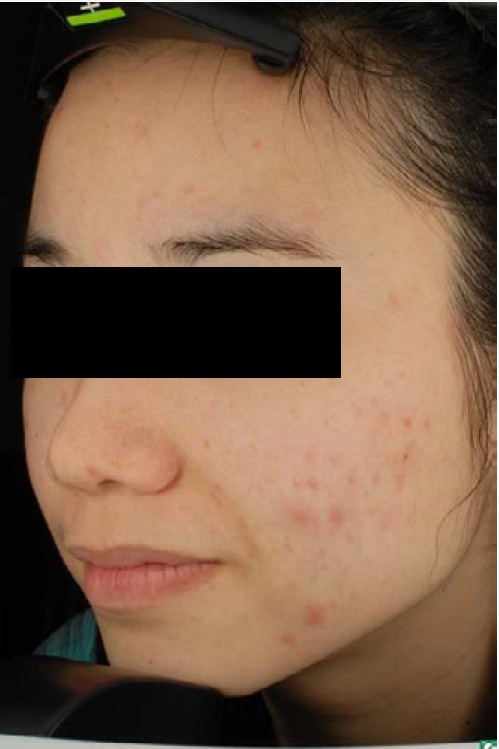
Figure 3:Acne Vulgaris Clinical Trial 400nm – 450nm QBM Blue
| Before | After |
 |
 |
|
|
|
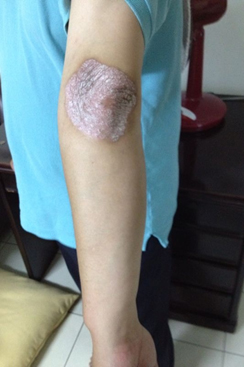
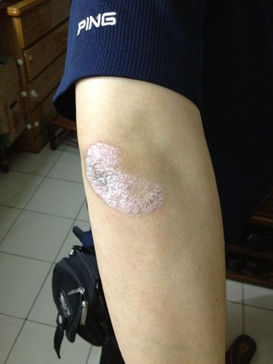
Figure 4: Psoriasis trial using 400nm – 450nm QBM Blue
| Before | After |
 |
 |
- For Specialists:
- Visible blue light therapy available from the use of QBM blue is a proven method to treat microbiological disease without side effects compare to other treatment types especially in large areas. ii. MRSA is the prime inducing factor for much of the skin conditions where light filtered by the QBM blue can be used to control and eradicate. iii. QBM blue is a FDA registered class 1 medical device with minimal risks. iv. For patients whose health can be effected by treatments (for example, TCS and infants), QBM blue offers a complete solution. b. For Consumers: i. QBM blue is proven to be a safe and effective method to treat acne, eczema and other skin conditions without the worry of side effects.
- MRSA is the prime inducing factor for much of the skin conditions where light filtered by the QBM blue can be used to control and eradicate.
- QBM blue is a FDA registered class 1 medical device with minimal risks.
- For patients whose health can be effected by treatments (for example, TCS and infants), QBM blue offers a complete solution.
- For Consumers:
- QBM blue is proven to be a safe and effective method to treat acne, eczema and other skin conditions without the worry of side effects.
- QBM blue is easy to use and ready to treat large area skin disorders.
[1] Becker, D., Langer, E., Seemann, M., Seemann, G., Fell, I., Saloga, J., Grabbe, S., Stebut, E.V., 2011. Clinical Efficacy of Blue Light Full Body Irradiation as Treatment Option for Severe Atopic Dermatitis.Department of Dermatology, University Medicine, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany. [PDF] Available at: < http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3110790/pdf/pone.0020566.pdf> [Accessed 26-12-2012]









Follow us